
We released the world's first comprehensive mollusc genome database
On October 23, 2020, Nucleic Acids Research published online the first comprehensive molluscan genomics database "MolluscDB: an integrated functional and evolutionary genomics database for the hyper-diverse animal phylum Mollusca".
The revolutionary breakthrough of high-throughput sequencing technology and the wide application of various omics technologies have brought unprecedented development opportunities for the field of life science, and promoted life science research to enter the era of big data. With the unprecedented growth of genomic data, deep mining of complex and high-dimensional massive omics resources has become a great challenge in the field of life science. The construction of convenient and comprehensive genomic databases plays an important role in solving this problem. Currently, the large public genome databases widely used in the world are still mainly focused on human medicine and model organism research such as mice, zebrafish, Drosophila and so on. For non-model organisms, such as most Marine organisms, there is still a lack of appropriate integration platforms and deep analysis tools to meet the growing demand for complex and massive omics data.
Molluscs originated in the Early Cambrian 500 million years ago and are one of the most evolutionarily successful groups of invertebrates. With more than 100,000 extant species, molluscs are the second largest phylum in the animal kingdom after arthropods, and the study of the origin and evolution of molluscs has long been a hot topic of academic interest. In addition, many mollusks are also economically important aquatic species, accounting for up to 22% of the world's total aquatic production. The rapid development of molluscan genomics in recent years has led to a number of important scientific discoveries that have greatly enhanced the current depth of knowledge on the origin and adaptive evolution of animals. Currently, molluscan genomics resources are usually stored in public databases such as NCBI in a raw data state, and there is a lack of comprehensive platforms for data integration and in-depth analysis, and a lack of customized analytical tools designed for molluscan biology. By extensively collecting mollusc genomics resources, systematically sorting and integrating multi-omics data and developing rich analysis tools, we constructed MolluscDB, the most extensive mollusc genomics analysis platform with the widest species coverage, the richest omics resources and the most comprehensive functions to date.

The home page of MolluscDB
MolluscDB has collected and integrated nearly 1000 omics data resources, including 20 high-quality reference genomes, 538 transcriptomes and 409 mitochondrial genomes. The data came from 123 species, covering 87% of all 7 classes and 53 orders of the phylum Mollusca. The geographical distribution covers land, freshwater, offshore and deep sea, and includes the majority of published mollusca omics resources. MolluscDB provides up to 10 basic omics analyses, including genome assembly information, phylogenetic relationships, ancient fossil record, gene sequence and structure, gene function annotation, developmental period/adult tissue expression profile, gene families, transcription factors and transposable elements. Convenient visualization of complex genomic information was achieved by developing a custom genome browser. MolluscDB also provides customized data sets and analysis tools to meet specific research needs, including developmental and adult gene co-expression networks, core gene sets of mollusc ancestors and their sub-taxa, and macrosynteny analysis. MolluscDB provides the most systematic and comprehensive molluscan genomics platform so far, which will enable the field of mollusc research field to cope with and make full use of the growing amount of massive genomic resources, thus accelerating the discovery of important genetic resources and promoting the cognition of the genetic evolutionary patterns of unique life processes of marine organisms, as well as providing strong support for shellfish genetic breeding efforts.
Professor Shi Wang of the Key Laboratory of Marine Genetics and Breeding, Ministry of Education, and Sars-Fang Centre is the corresponding author, Associate Professor Yuli Li is the co-corresponding author, and PhD student Fuyun Liu is the first author of this paper. The research work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and Taishan Scholar Project Fund of Shandong Province of China. This work was also supported by the Center for High Performance Computing and System Simulation (Qingdao Pilot National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology).
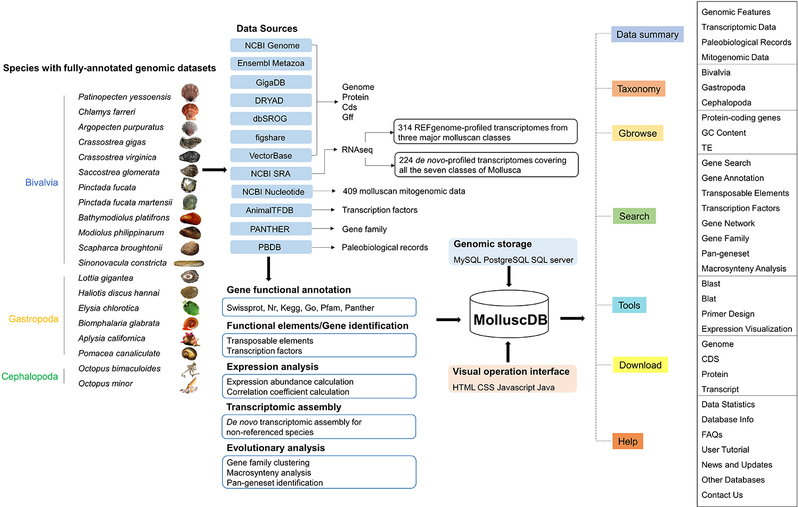
Overview of MolluscDB database structure and web interface features
Paper links: https://academic.oup.com/nar/advance-article-abstract/doi/10.1093/nar/gkaa918/5936037

