
We released the first evo-devo multi-omics database platform across the animal kingdom
On November 1, 2022, our group and Professor Dong Bo's team jointly published "EDomics: a comprehensive and comparative multi-omics database for animal evo-devo "(http://edomics.qnlm.ac), which released the first evo-devo multi-omics database and comprehensive analysis platform across the major evolutionary node groups in the entire animal kingdom.
Evolutionary developmental biology (EvoDevo) is a rapidly emerging interdisciplinary discipline that aims to study the highly diverse developmental processes in the biological world, so as to deeply summarize and interpret the hidden evolutionary driving mechanisms and laws behind the developmental processes, and to answer the question of biodiversity-determining mechanisms, which was named as one of the 125 most challenging scientific problems by Science. In the past few decades, extensive studies that used well-established model organisms (e.g. Drosophila melanogaster, Caenorhabditis elegans, Danio rerio and Mus musculus) have, have led to many major discoveries and breakthroughs in biology, laying the foundation for the current framework of knowledge in genetics, development, and evolution. However, the few model animals cannot cover all the information of the highly diverse developmental processes in the animal kingdom, much less provide a panoramic interpretation and generalization of the developmental evolution of the entire animal kingdom. In filling this great knowledge gap, the use of emerging new model organisms with key phylogeny positions and full-spectrum coverage shows great application potential by revolutionizing the evo-devo field to depict the whole history of developmental evolution across the tree of life, which will drive the leapforward development of evolutionary development. The revolutionary breakthrough of high-throughput sequencing technology and the wide application of various omics technologies have brought unprecedented development opportunities for the field of life science. Genomics, transcriptomics, and single-cell technologies have sped up the development of many traditional non-model organisms into new model organisms (e.g. ctenophore Mnemiopsis leidyi, placozoan Trichoplax adhaerens, ascidian Ciona robusta and mollusc Patinopecten yessoensis). Although large amounts of multi-omics resources have been accumulated, which are rapidly increasing in diverse animal groups, integrative access and utilization of these scatteredly deposited genomic resources pose a great challenge for the animal evo-devo research community. There is an urgent need to systematically establish an evolutionary-developmental integrative multi-omics database and corresponding convenient tools for the entire animal kingdom.
To achieve this goal, the research team collected and integrated a large amount of genomic, transcriptomic, single-cell and spatial transcriptomic data resources of traditional and emerging nonstandard model organisms across the entire animal kingdom, established a unified standard, categorized and processed the massive data of multiple species, broke the bottleneck of cross-species multi-omics data comparison, and built the first international comprehensive multi-omics database platform for animal evolution and development ( EDomics, http://edomics.qnlm.ac) EDomics database represents the most comprehensive and comprehensive developmental and evolutionary multi-omics resources to date, including 40 high-quality genomes and 1010 bulk transcriptomes from 21 major animal phyla, representing species from major groups across the entire animal kingdom. And 68 single-cell transcriptomes covering 429 cell types from 12 well-studied species. The animal species that are selected involve the major developmental and evolutionary events, including the presence of different germ layers, formation of radial and bilateral symmetry, and protostome-to-deuterostome, water-to-landing and invertebrate-to-vertebrate evolutionary transition (Figure 1).
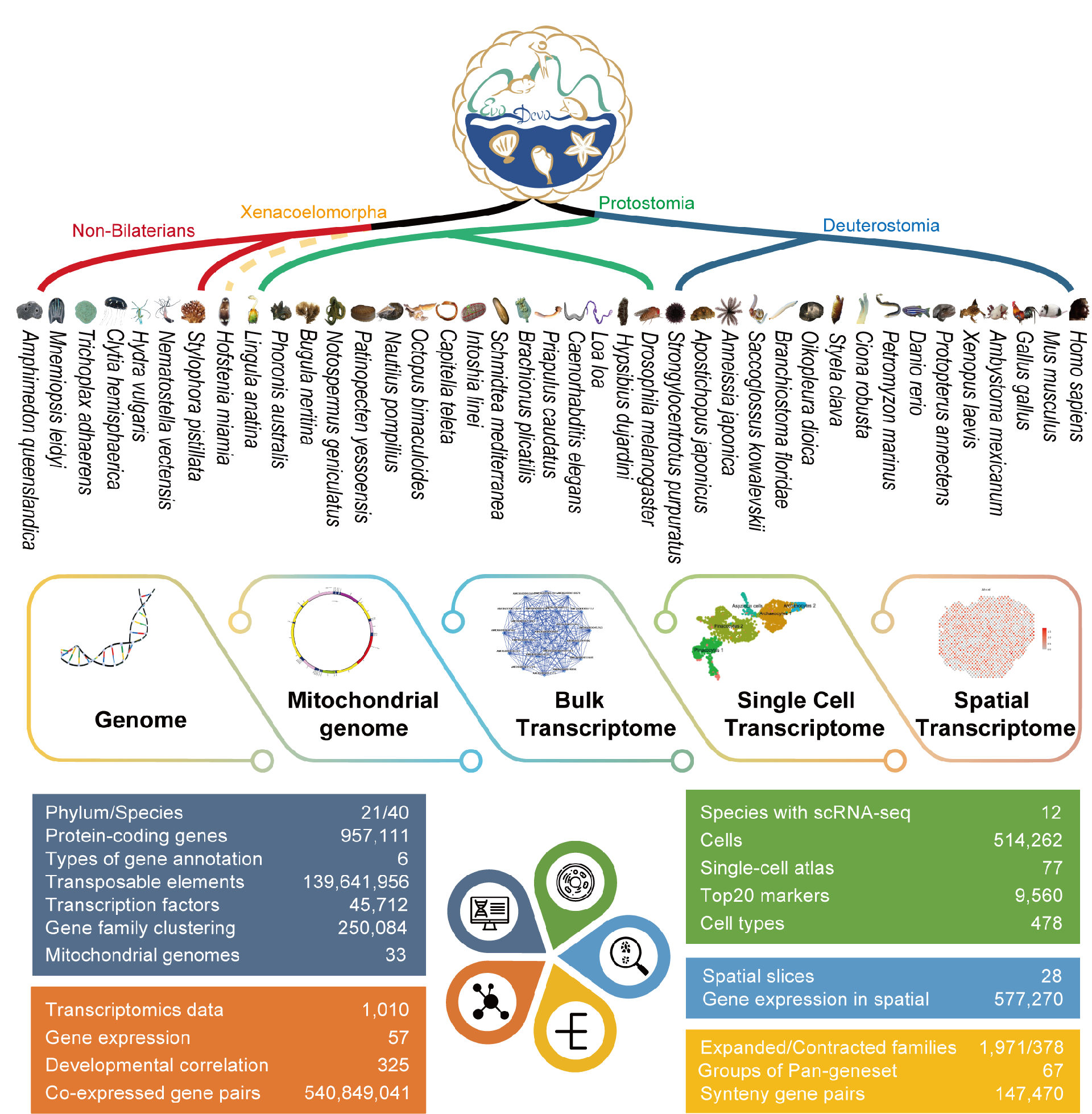
Figure 1 Overview of EDomics and summary of data composition
EDomics database not only provides high-quality multi-omics information (including genome assembly, genome annotation, gene family clustering, mitochondrial genome, gene expression profiles, and gene co-expression networks of various developmental stages and adult tissues/ organs), but also multi-dimensional single-cell omics information (such as cell atlas, cell markers, gene expression, and gene spatial-map information). It also provides powerful bioinformatics tools. These tools enable the exploration and comparative analysis of evolutionary information (such as gene family expansion/ contraction, core and dispensable geneset, macrosynteny analysis, and developmental correlation analysis) among different animal groups. In addition, the customized tools provided by the database allow efficient cross-species omics data analysis and cell lineage tracking (Figure 2).
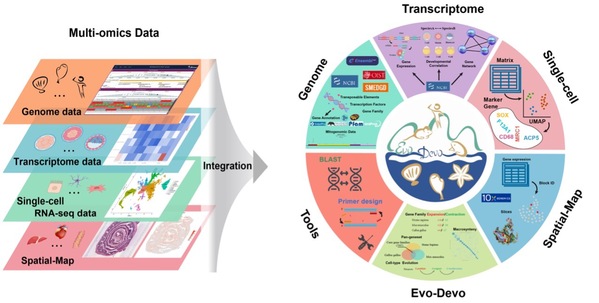
Figure 2 Multi-omics data and cross-species analysis are integrated into six main modules in EDomics
The EDomics database can provide a systematic display of genomics and transcriptomics information from the entire animal kingdom, and provide a valuable and unique platform to describe the major transformations in developmental processes and innovative changes in biological evolution. The establishment of EDomics will provide an open access platform with the widest species coverage, richest omics resources, and most comprehensive analysis functions for the international community of animal evolution and development, and realize the systematic integration and in-depth analysis of the rapidly growing evo-devo massive omics resources to promote innovative discoveries and breakthroughs in the field of life science. Finally, it depicts the whole picture of the development and evolution of the whole tree of life.
The publication of the above research results provides an important resource platform for the field of animal evolution and development. During the review of the article, the international peers gave a high evaluation " The authors presented an integrative multi-omics database EDomics for animal evo-devo, which is very impressive”; " These might be very useful tools for future studies in EvoDevo field especially recently published data of scRNA-seq and also spatial expression map ". This project is another important milestone after our team published the first comprehensive mollusc genome database 'MolluscDB': an integrated functional and evolutionary genomics database for the hyper-diverse animal phylum Mollusca, (http://mgbase.qnlm.ac, Nucleic Acids Research 2021).
Professor Dong Bo, Professor Wang Shi, and Associate Professor Li Yuli of Sars-Fang Centre were the common corresponding author, Dr. Jiankai Kui, master student Penghui Liu, and doctoral student Fuyun Liu are the co-first authors of the paper, and other members of the center participated in the research and development work of this project. The above work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, the Marine S&T Fund of Shandong Province for the National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Key R&D Project of Shandong Province, and the Taishan Scholar Program of Shandong Province. This work was also supported by the Center for High Performance Computing and System Simulation (Qingdao Pilot National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology).
Paper links:
Jiankai Wei†, Penghui Liu†, Fuyun Liu†, An Jiang, Jinghan Qiao, Zhongqi Pu, Bingrou Wang, Jin Zhang, Dongning Jia, Yuli Li*, Shi Wang* and Bo Dong* EDomics: a comprehensive and comparative multi-omics database for animal evo-devo.Nucleic Acids Research. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac944

